# Content Security Policy
There is a meta tag that you should put into ALL your websites and web apps and hybrid apps. It is a security feature to protect your users.
It has the http-equiv attribute set to Content-Security-Policy and then a content attribute with all the possible values of where the browser is allowed to load different types of resources from.
<meta http-equiv="Content-Security-Policy" content="default-src https: ;" />
The value inside content is broken up into different categories like default-src, img-src, style-src, font-src, media-src, and connect-src. After each category name you put one or more values for allowed sources for that type of content. After each source list you put a semi-colon.
See the CSP website for the full list of categories and values. CSP website official reference
You should put this meta tag into EVERY webpage you build.
When things go wrong with your Content-Security-Policy you will see notifications in the JavaScript console in the browser.
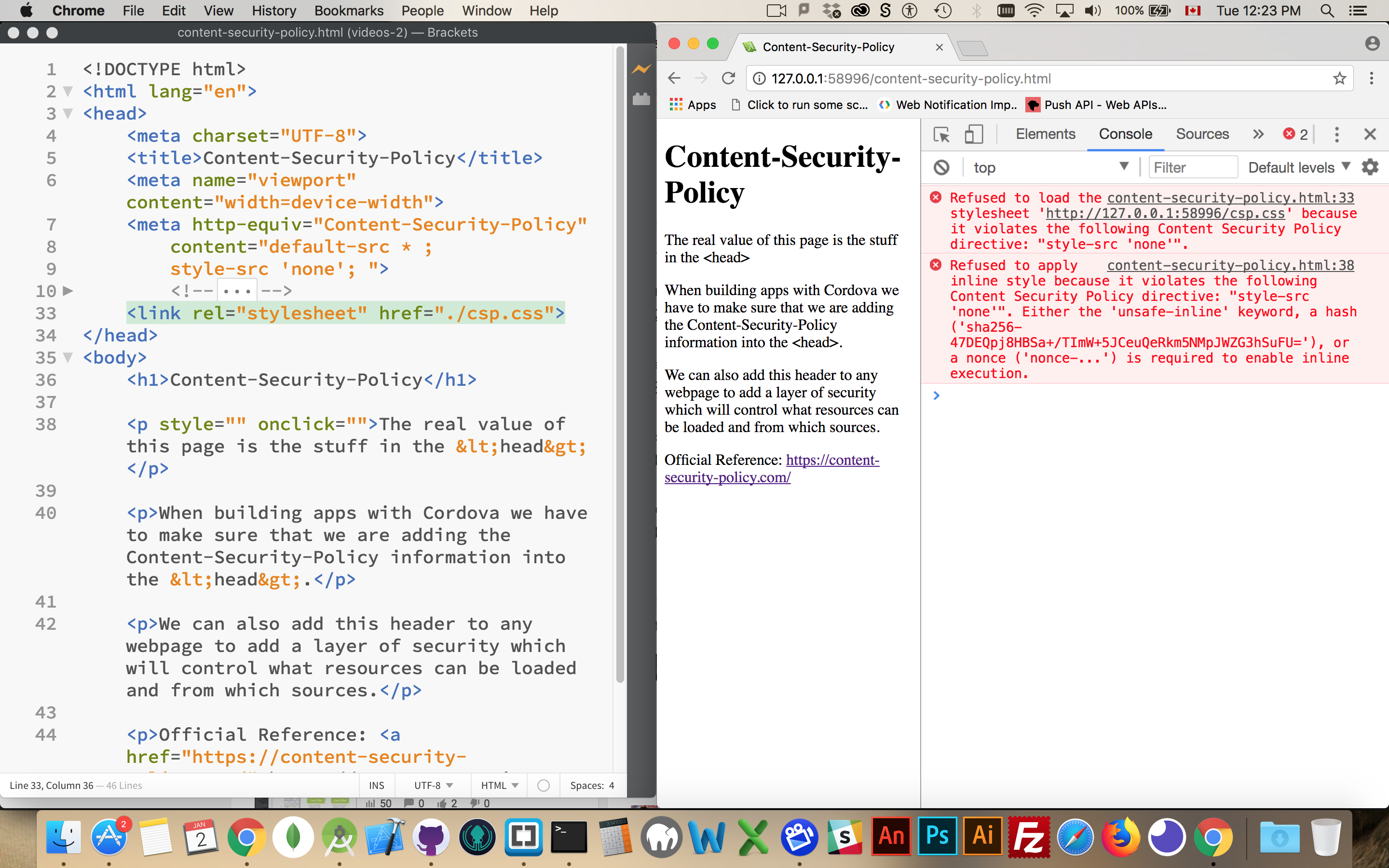
In this screenshot it is saying that it cannot load the stylesheet because the style-src is set to "none".
When you run into problems with the CSP, you should just respond to each error separately by adding a new category or updating a category to include a specific location. While you can just put everything into default and accept anything this defeats the purpose and provides no security for your users.
# Using the Script integrity Attribute
With script tags, we can add an integrity attribute which helps protect our users further. This attribute value also needs to be added to your CSP tag.